Tiny living machines identified as xenobots can build copies of by themselves
Tiny “living machines” designed of frog cells can replicate on their own, producing copies that can then go on to do the same. This newly explained form of renewal offers insights into how to style biological devices that are self-perpetuating.
“This is an very remarkable breakthrough,” for the industry of biologically centered robotics, says Kirstin Petersen, an electrical and computer system engineer at Cornell College who scientific studies groups of robots. Robots that can copy themselves are an essential move toward techniques that never have to have people to operate, she suggests.
Before this year, researchers explained the behaviors of the lab-made residing robots, termed xenobots (SN: 3/31/21). Plucked out of frogs’ expanding bodies, smaller clumps of pores and skin stem cells from frog embryos knitted themselves into smaller spheres and started to move. Cellular extensions called cilia served as motors that run the xenobots as they cruised all-around their lab dishes.
That cruising can have a even larger intent, the researchers now report in the Dec. 7 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. As the xenobots bumble about, they can get loose frog cells into spheres, which then coalesce into xenobots by themselves.
This form of motion-developed copy, referred to as kinematic self-replication by the scientists, seems to be new for dwelling cells. Normally, reproducing organisms contribute some parental substance to their offspring, states analyze coauthor Douglas Blackiston of Tufts University in Medford, Mass., and Harvard College. Sexual copy, for occasion, needs parental sperm and egg cells to get started. Other styles of reproduction contain cells splitting or budding off from a dad or mum.
“Here, this is different,” Blackiston suggests. These xenobots are “finding loose components, sort of like robotics sections in the environment, and cobbling them alongside one another.” All those collections then mature into “a next generation of xenobots that can move close to like their parents,” Blackiston says.
https://www.youtube.com/enjoy?v=e9krifazZA0
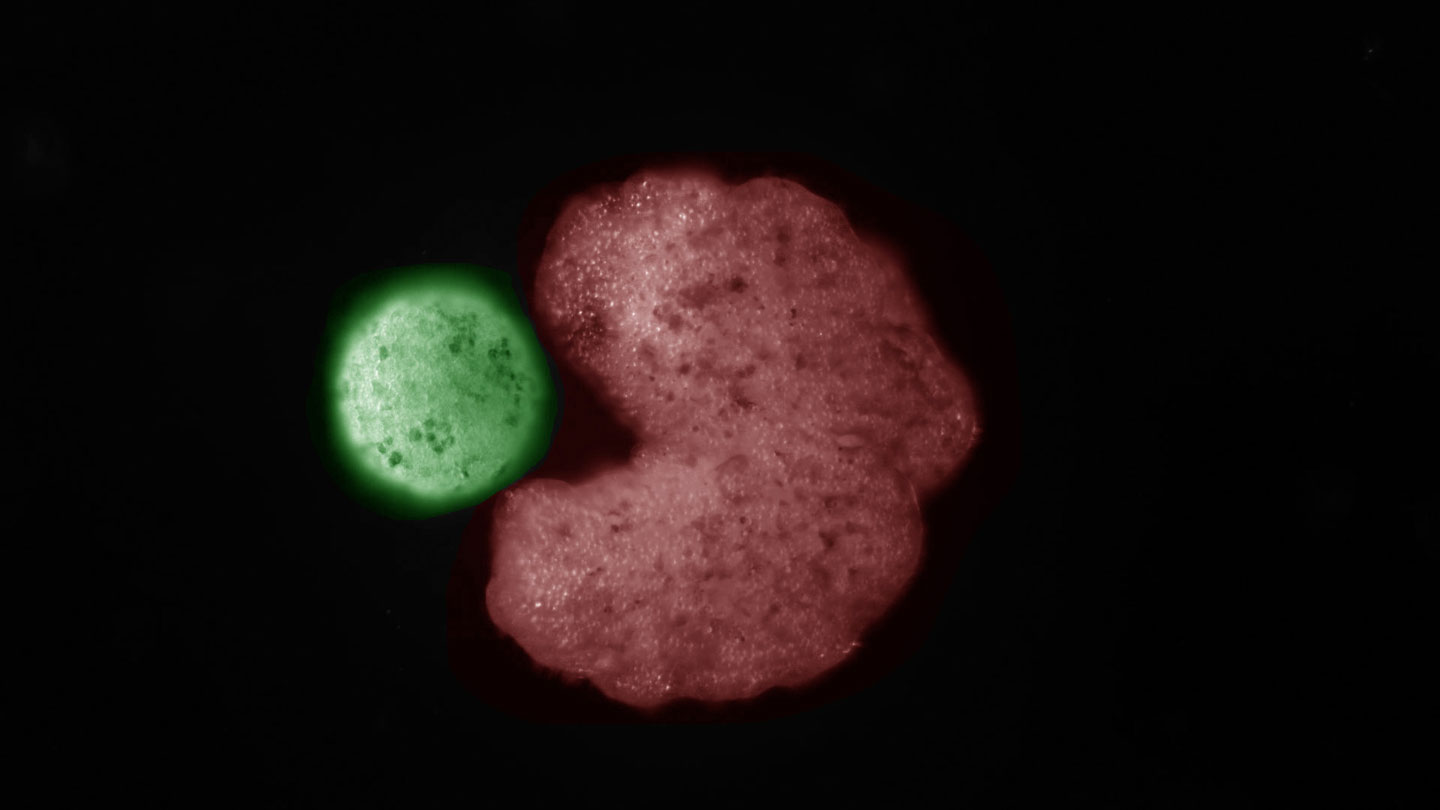
Left to their very own products, spheroid xenobots could normally build only a person a lot more technology just before dying out, the scientists identified. But with the assistance of an synthetic intelligence method that predicted an exceptional form for the initial xenobots, the replication could be pushed to four generations.
The AI application predicted that a C condition, considerably like an openmouthed Pac-Male, would be a much more productive progenitor. Guaranteed adequate, when improved xenobots have been permit free in a dish, they commenced scooping up loose cells into their gaping “mouths,” forming much more sphere-shaped bots. A cell offspring took form the moment about 50 cells had glommed together in a parent’s opening, Blackiston states. A comprehensive-bodied xenobot is composed of about 4,000 to 6,000 frog cells.
Xenobots’ small measurement is an advantage, Petersen suggests. “The simple fact that they have been equipped to do this at this kind of a modest scale just will make it even far better, mainly because you can start to think about biomedical software areas,” she suggests. Minuscule xenobots may possibly be equipped to sculpt tissues for implantation, for occasion, or go inside of bodies to provide therapeutics to precise spots.
Over and above the probable positions for the xenobots, the investigation advances an significant science, one that has existential worth for individuals, claims examine coauthor Michael Levin, a developmental biologist at Tufts. That is, “the science of attempting to foresee and regulate the repercussions of sophisticated techniques,” he says.
“Originally, no 1 would have predicted any of this,” Levin claims. “These things are routinely performing things that shock us.” With xenobots, researchers can drive the limits of the surprising. “This is about a safe and sound way to investigate and advance the science of staying significantly less astonished by issues,” Levin states.







