How 2021 analysis confirmed mating throughout teams drove human evolution
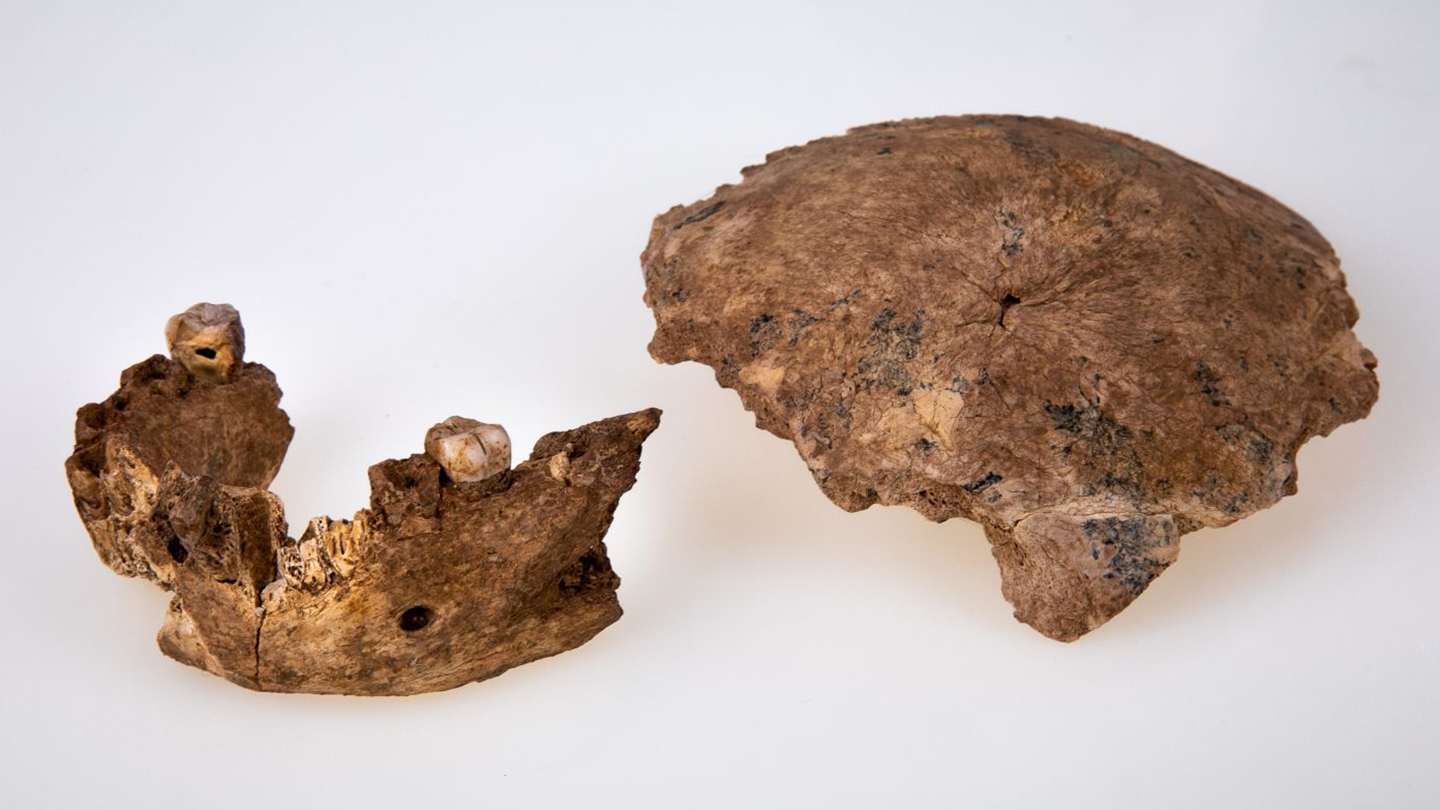

Evidence that cross-continental Stone Age networking situations run human evolution ramped up in 2021.
A long-standing argument that Homo sapiens originated in East Africa before transferring in other places and changing Eurasian Homo species these types of as Neandertals has come beneath increasing fireplace over the very last decade. Research this yr supported an alternative scenario in which H. sapiens developed across extensive geographic expanses, 1st inside Africa and later outdoors it.
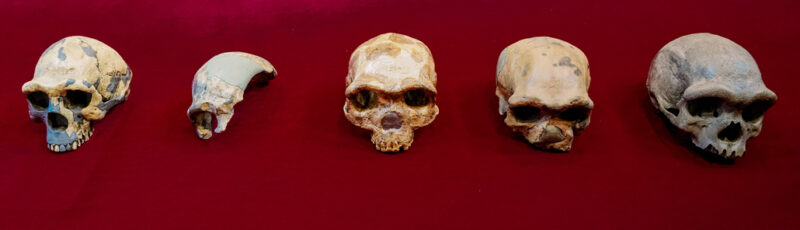
The procedure would have labored as follows: Quite a few Homo teams lived throughout a time period recognized as the Center Pleistocene, about 789,000 to 130,000 several years ago, and were being as well intently linked to have been unique species. These groups would have occasionally mated with each individual other although touring by Africa, Asia and Europe. A selection of skeletal versions on a human theme emerged among significantly-flung communities. Human anatomy and DNA these days incorporate remnants of that sophisticated networking legacy, proponents of this circumstance say.
It’s not crystal clear exactly how generally or when throughout this time period teams may have blended and mingled. But in this framework, no obvious genetic or actual physical dividing line separated Middle Pleistocene individuals commonly classed as H. sapiens from Neandertals, Denisovans and other historic Homo populations.
“Middle Pleistocene Homo groups had been people,” claims paleoanthropologist John Hawks of the College of Wisconsin–Madison. “Today’s people are a remix of those historic ancestors.”
New fossil proof in line with that thought arrived from Israel. Braincase items and a lessen jaw made up of a molar tooth unearthed at a web-site known as Nesher Ramla day to concerning about 140,000 and 120,000 yrs in the past. These finds’ attributes propose that a formerly unidentified Eurasian Homo populace lived at the site (SN Online: 6/24/21), a workforce led by paleoanthropologist Israel Hershkovitz of Tel Aviv University documented. The fossils have been discovered with stone equipment that glimpse like all those fashioned about the similar time by Middle Easterners commonly labeled as H. sapiens, suggesting that the two groups culturally mingled and probably mated.
Interactions like these might have facilitated sufficient mating amid mobile Homo populations to prevent Nesher Ramla inhabitants and other Eurasian groups from evolving into independent species, Hershkovitz proposed.
But one more report delivered a reminder that views continue to change about irrespective of whether Middle Pleistocene Homo evolution showcased relevant populations that all belonged to the exact species or distinct species. Researchers studying the strange blend of options of a roughly 146,000-year-outdated Chinese cranium dubbed it a new species, Homo longi (SN On the net: 6/25/21). Immediately after examining that declare, on the other hand, a further investigator grouped the cranium, nicknamed Dragon Person, with quite a few other Middle Pleistocene Homo fossils from northern China.
If so, Dragon Gentleman — like Nesher Ramla Homo — may well hail from just one of several intently similar Homo strains that from time to time mated with each other as some groups moved through Asia, Africa and Europe. From this point of view, Center Pleistocene Homo groups advanced special traits all through durations of isolation and shared options as a consequence of crossing paths and mating.
Back again-and-forth migrations by Homo groups concerning Africa and Asia begun at the very least 400,000 several years back, discoveries in Saudi Arabia suggest (SN: 10/9/21 & 10/23/21, p. 7). Monsoon rains periodically turned what’s now desert into a green passageway lined by lakes, wetlands and rivers, documented archaeologist Huw Groucutt of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human Historical past in Jena, Germany, and colleagues. Each and every of 5 historical lake beds discovered at a Saudi web site when hosted hunter-gatherers who remaining powering stone instruments.
Occupations occurred intermittently concerning about 400,000 and 55,000 a long time ago. By about 200,000 many years back, stone instruments at a single of the lake beds resembled those designed all around the similar time by H. sapiens in northeastern Africa. Some of those Africans could have stopped for a little bit in a environmentally friendly Arabia just before trekking into southwestern Asia, Groucutt indicates.
Either H. sapiens or Neandertals made stone resources unearthed in the youngest lake mattress. Neandertals inhabited sections of the Middle East by around 70,000 years ago and could have arrived at a perfectly-watered Arabia by 55,000 many years in the past. If which is what happened, Neandertals may perhaps have mated with H. sapiens already there, Groucutt speculates.
Although Arabian hookups have but to be detected in historical DNA, European Neandertals and H. sapiens mated incredibly normally all-around 45,000 years in the past (SN: 5/8/21 & 5/22/21, p. 7), other researchers noted. DNA extracted from H. sapiens fossils of that age uncovered in Bulgaria and the Czech Republic suggests that these ancient persons possessed between about 2 % and 4 % Neandertal ancestry, a big total taking into consideration H. sapiens migrants experienced only not too long ago arrived in Europe.
So even soon after the Center Pleistocene, networking between ancient Homo teams may possibly have served make us who we are currently.







